Deep Mutual Learning
04 Apr 2019 | Deep learningDeep Mutual Learning
Original paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.00384.pdf
Authors: Ying Zhang, Tao Xiang, Timothy M. Hospedales, Huchuan Lu
Abstract
- Model distillation은 teacher의 정보를 student network로 전달하도록 많이 사용되는 효과적인 기술이다. 일반적으로 small network로 성능좋고 큰 네트워크나 앙상블 네트워크를 transfer 하는것은 low-memory나 빠른 동작이 필요할 때 더 필요하다. 본 논문에서는 미리 학습(정의된) teacher와 student 사이에 단 방향으로 transfer 되는 방식이 아닌 student의 앙상블이 협력적으로 training 과정 전반에 걸쳐 서로를 가르치는 deep mutual learning(DML) strategy를 제안한다. 실험에서는 논문에서 제안하는 mutual learning이 다양한 network 구조에 대해 CIFAR-100 recognition과 Market-1501 person re-identification benchmark에서 매우 좋은 결과를 보였다. 논문에선 이전처럼 표현력 좋은 강력한 teacher network가 필요하지 않다는 것을 밝혔다. 단순히 student network들로 이루어진 collection간에 서로 상호 학습을 하도록 하는것이 더 효과적이며, 더욱 강력하면서도 teacher net의 distillation보다 더 좋은 성능을 보여준다.
1. Introduction
- Deep neural network는 다양한 분야에서 SOTA 성능을 보였지만 대개는 depth나 width가 넓어 많은 파라미터들을 갖고 있다[6, 25]. 이는 연산량이 많아 속도가 느리거나 메모리를 많이 필요로하므로 제한된 성능을 갖는 환경에서의 적용이 어렵다. 따라서 빠른 모델을 만들어내는 연구가 활발히 진행되었다. 크기는 작지만 정확한 모델을 얻는방법에 대해 간단한(frugal) 모델 설계[8], model compression[2], pruning[13], binarisation[18], model distillation[7]등의 연구가 진행되었다.
- Distillation based 모델 압축방식은 작은 네트워크가 대때로 큰 네트워크만큼의 표현량(representation capacity)을 갖는 경우가 많다는 obwervation과 관계되어 있다[3, 2]. 하지만 큰 네트워크와 비교했을 때 desired function을 실현시키는 올바를 파라미터를 갖도록 모델을 학습시키고 찾는것은 더 어려워지게 된다. 즉 limitation은 네트워크의 크기보다 적절한 optimization을 하는것이 더 어려운 문제다[2]. 작은 네트워크를 잘 학습시키기 위한 distillation 방법에서는 deep하고 wide하거나 앙상블로 이루어진 teacher net이 필수요소이며 작은 student network는 이러한 teacher net을 흉내내도록 학습되어진다 [7, 2, 16, 3]. Teacher net의 class probabilities[7]나 feature representation[2, 19]을 흉내내거나 하는것은 기존의 supervised learning target의 목표를 넘어 추가적인 정보를 이용 할 수 있게 되는것이다. Teacher를 흉내내도록 학습시키기 위한 optimization 문제는 target function을 다이렉트로 학습하는것보다 더 쉬운 것으로 밝혀졌으며, 이로인해 훨씬 작은 student가 larger teacher의 성능 또는 그 성능을 능가할 수 있게 된다[19].
- 논문에선 model distillation과 관련되었지만 다른 방법을 제안하며, 이를 mutual learning으로 정의한다. Distillation에선 성능좋고 큰 pretrained teacher network가 필수이며 작고 학습되지 않은 student net에 한 방향으로 정보를 전달하며 학습시킨다. 반면에 mutual training에서는 동시에 task를 같이 해결하도록 학습되어지는 untrained student network들(pool)이 필수요소이다. 특히 각 student는 두 개의 loss로 학습되어지며, 하나는 일반적인 supervised learning loss이고 다른 하나는 mimicry loss이며 이는 다른 student들의 class별 확률을 사용하는 각 student의 class posterior를 정렬하는 역할을 한다. 이러한 peer-teaching based scenario방법으로 학습 되는 student가 기존의 supervised learning scenario로 단독학습한 모델보다 훨씬 더 좋은 성능을 보이는 것을 확인했다. 게다가 이런 방식으로 학습 된 student net들은 기존의 pre-trained teacher를 사용하는 distillation 방법보다 더 나은 성능을 보였다. 또한 학습시키려는 student보다 더 크고 성능 좋은 teacher를 필요로하는 기존의 distillation방법에 있어서 다양한 몇몇의 큰 네트워크간의 mutual learning이 단독학습보다 더 성능을 크게 개선시키는것을 확인했다.
- 제안하는 방법이 왜 항상 제대로 동작하는지 확실하지는 않다. 모델 학습 과정에서 작고 학습되지 않은 student network들에 대해 어디서 추가정보가 제공되었을까? 왜 모델이 학습과정에서 ‘the blind lead the blind’처럼 학습을 방해하지 않고 잘 수렴하게 될까? 질문에 대한 몇몇 답변들은 직관적으로 다음의 사항들에 대해 얻어질 수 있다. 각 student는 주로 일반적은 supervised learning에 의해 학습되어 지므로 성능이 일반적으로 향상되어지도록 학습되어지므로 이로인해 student 그룹이 마음대로 학습되어질 수 없게 되는것이다. Supervised learning 방법을 통해 모든 네트워크가 학습과정에서 올바른 추론을 할 수 있도록 학습되어지게된다. 하지만 각 네트워크는 서로다른 initial condition에서 학습이 시작되어지므로 각 모델이 추론하는 결과가 class별로 다양해지게 된다. 또한 mutual learning 뿐만 아니라 distillation[7]에서 얻어지는 추가정보도 2차적으로 사용한다(?)(It is these secondary quantities that provide the extra information in distillation [7] as well as mutual learning). Mutual learning에서 student chort(집단)는 다음으로 가장 정답일 가능성이 높은 class에 대한 collective estimate를 효과적으로 모으게 된다. Finding out - and matching 하는 다른 students들에 따라 각 traning instace의 다른 가장 가능성있는 클래스가 각 student의 posterior entropy를 증가시키며[4, 17] 이는 student가 더 fobust하고 flatter한 minima에 수렴해 testing data에 generalization이 잘 되도록 한다. 이는 deep learning에서 high posterior entropy solutions(network parameter settings)의 rubustness에 관한 최근의 연구들과 관련이 있지만[4, 17], blind entropy regularization보다 훨씬 더 많은 선택이 가능한 대안들이 존재한다.
- 전반적으로 mutual learning은 다른 네트워크 집단(cohort)과의 협력을 통해 네트워크의 generalization 성능을 향상시킬 수 있는 간단하면서도 효과적인 방법을 제공한다. 미리 훈련 된 static large network를 사용하는 distillation 방법과 비교할 때, 작은 peer들의 협력적인 학습방법은 더 나은 성능을 달성한다. 게다가 논문에선 다음의 사항들을 시사한다.
- (1) Cohort 네트워크의 갯수에 따라 성능이 증가한다.(효율적 mutual learning을 위해 작은 네트워크를 이용하여 하나의 GPU에서 학습이 가능하다)
- (2) 다양한 네트워크 아키텍쳐와 크고 작은 네트워크로 이루어진 이종(heterogeneous) cohort에도 적용 가능하다.
- (3) Cohort에서 large network가 mutual learning을 사용한 방법이 단독학습한것보다 성능이 더 좋다.
- 마지막으로 논문에선 하나의 effective한 네트워크를 얻는데 초점을 맞추지만 전체 cohort를 매우 효과적인 앙상블 모델로도 사용할 수 있다.
Related Work
- Distillation based 모델압축방법은 한참옛날에 [3]에서 제안되었지만 이게 왜 동작하는지 직관적으로 설명하는 7로 인해 요즘 다시 재고되고 있다. 처음엔 성능 좋거나 앙상블로 구성된 teacher에 의해 근사화된 함수를 단일 신경망 student net으로 distillation하는 것이 일반적인 적용방법이었다[3, 7]. 하지만 나중엔 학습이 쉬운 큰 성능좋은 네트워크를 distillation하여 작지만 학습이 어려운 네트워크로 적용시켜 teacher의 성능을 능가하게까지 만들었다[19, FitNet]. 최근에는 [15]와 SVM+[22]와 같은 information learning theory를 이용하여 distillation이 더 systematically하게 teacher에서 선별된 정보를 student로 전달한다. 저자는 teacher와 함께 dispensing하고 student들의 앙상블이 서로 distillation하여 서로를 가르치도록 하였다.
- Other related ideas include Dual Learning [5] where two cross-lingual translation models teach each other interactively. But this only applies in this special translation problems where an unconditional within-language model is available to be used to evaluate the quality of the predictions, and ultimately provides the supervision that drives the learning process. In contrast, our mutual learning approach applies to general classification problems. While conventional wisdom about ensembles prioritises diversity [12], our mutual learning approach reduces diversity in the sense that all students become somewhat more similar by learning to mimic each other. However, our goal is not necessarily to produce a diverse ensemble, but to enable networks to find robust solutions that generalise well to testing data, which would otherwise be hard to find through conventional supervised learning.
2. Deep Mutual Learning
- Figure 1은 두 네트워크를 이용한 DML 적용방법에 대해 설명한다.
2.1 Formulation
- 자세한 수식적인것은 논문에서..
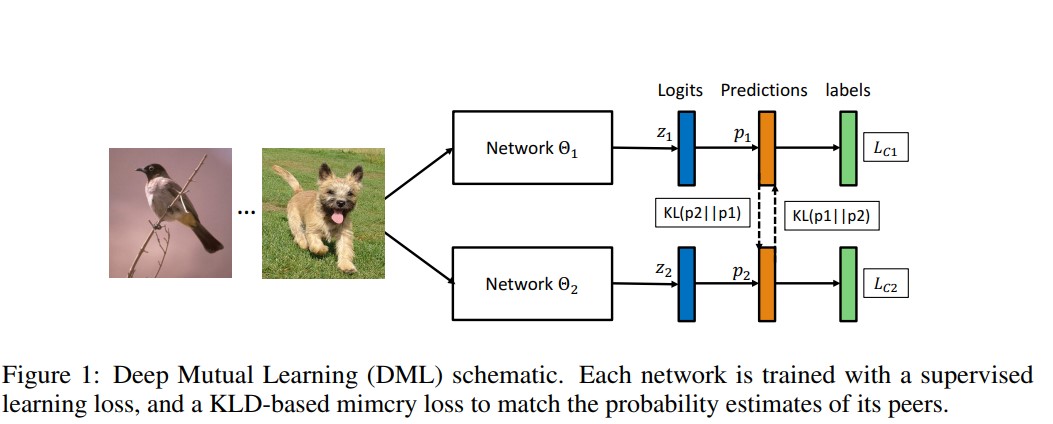
- 대략적으로, Cross entropy loss를 이용하여 각 네트워크의 prediction인 $p_{1}$ 과 $p_{2}$을 계산한다.
- 각 모델 $\Theta_{1}$의 testing에서 성능을 높히기 위해 다른 peer 네트워크인 $\Theta_{2}$을 이용한다. $\Theta_{2}$는 posterior probability인 $p_{2}$의 형식으로 training experience를 제공한다. 각 네트워크의 prediction인 $p_{1}$ 과 $p_{2}$의 match를 계산하기 위해 Kullback Leibler Divergence (KLD)를 사용한다.
- 이 과정에서 각 네트워크는 training instance에 대하여 정답인 true label에 대해 학습하면서도 peer가 추론한 probability도 학습하게 된다.
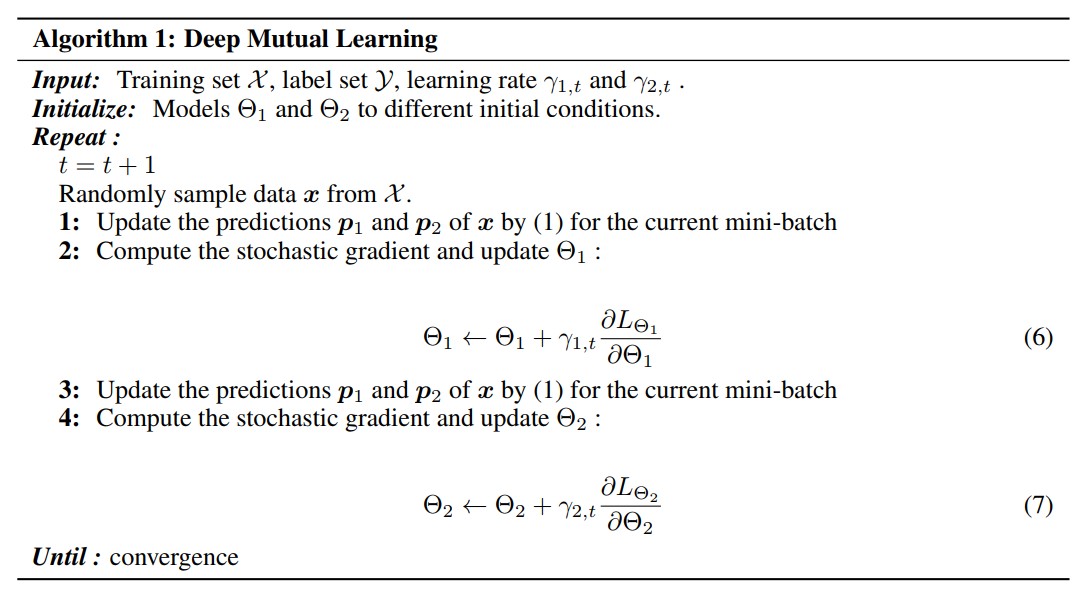
2.2 Optimization
- Optimization summury는 아래의 그림에서 설명된다.
2.3 Extenstion to Larger Student Cohorts
- 자세한 수식은 논문에서..
- 제안하는 DML을 통해 2개보다 더 많은 student를 cohort로 만들 수 있다.
- Network를 위의 $\Theta_{1}$과 $\Theta_{2}$에서 총 K개까지 늘리면 된다.(K는 자연수)
- 2개를 초과하는 network의 optimization 또한 Algorithm 1의 연장선상이다.
- 두개를 초과하는 네트워크에 대해 모든 K-1개의 네트워크들을 하나의 teacher로 만들면 되며, prediction은 다른 네트워크의 prediction들의 평균값을 취하여 $p_{avg}$ 형태로 전달하여 KLD를 계산한다.
- Section 3.6에서 single ensemble teacher나 DML_e를 사용하는 DML stratege는 위의 K-1 teacher를 사용하는 DML보다 성능이 떨어진다. 그 이유는 teacher ensemble을 teacher의 posterior probabilities를 true class에 대해 더 peak값을 갖도록 하는 model average step(위에서 prediction의 평균 취하는 과정)에서 모든 다른 class들에 대해 posterior entropy를 감소시키기 때문이다.
3. Experiment
3.1 Datasets and Settings
Datasets
- Two datasets are used in our experiments. The CIFAR-100 [11] dataset consists of 32×32 color images drawn from 100 classes, which are split into 50,000 train and 10,000 test images. The Top-1 classification accuracy is reported. The Market-1501 [27] dataset is widely used in the person re-identification problem which aims to associate people across different non-overlapping camera views. It contains 32,668 images of 1,501 identities captured from six camera views, with 751 identities for training and 750 identities for testing. As per state of the art approaches to this problem [28], we train the network for 751-way classification and use the resulting feature of the last pooling layer as a representation for nearest neighbour matching at testing. This is a more challenging dataset than CIFAR-100 because the task is instance recognition thus more fine-grained, and the dataset is smaller with more classes. For evaluation, the standard Cumulative Matching Characteristic (CMC) Rank-k accuracy and mean average precision (mAP) metrics [27] are used.
Implementation Details
- We implement all networks and training procedures in TensorFlow [1] and conduct all experiments on an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 GPU. For CIFAR-100, we follow the experimental settings of [25]. Specifically, we use SGD with Nesterov momentum and set the initial learning rate to 0.1, momentum to 0.9 and mini-batch size to 64. The learning rate dropped by 0.1 every 60 epochs and we train for 200 epochs. The data augmentation includes horizontal flips and random crops from image padded by 4 pixels on each side, filling missing pixels with reflections of original image. For Market-1501, we use Adam optimiser [10], with learning rate lr = 0.0002, β1 = 0.5, β2 = 0.999 and a mini-batch size of 16. We train all the models for 100,000 iterations. We also report results with and without pre-training on ImageNet.
Model Size
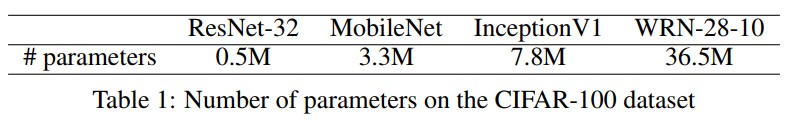
- The networks used in our experiments includes compact networks of typical student size: Resnet-32 [6] and MobileNet [8]; as well as large networks of typical teacher size: InceptionV1 [21] and Wide ResNet WRN-28-10 [25]. Table 1 compares the number of parameters of all the networks on CIFAR-100.
3.2 Results on CIFAR-100
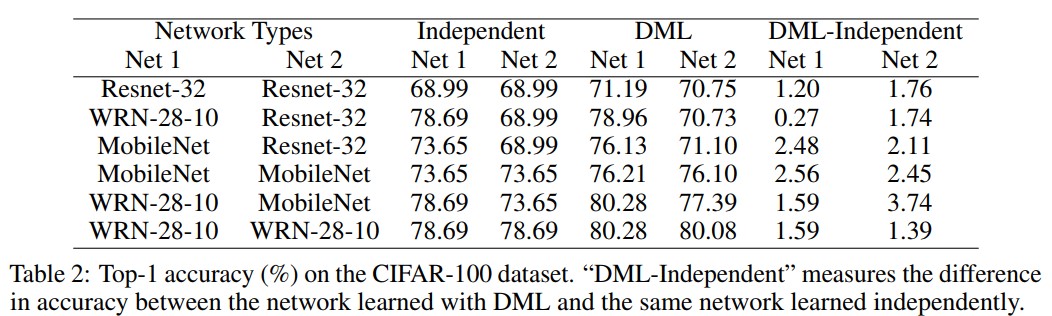
- Table 2는 다양한 구조를 사용하는 two-network DML cohort에 대한 CIFAR-100의 Top-1 accuracy다. 표에서 다음의 observation들을 확인 가능하다.
- (1) 모든 서로다른 네트워크는 ResNet-32, MobileNet, WRN-28-10중 하나며 그 조합들은 “DML-Independent” 열(column)에서 양수값을 나타내고, 이는 독립적으로 학습했을때에 비해 그만큼의 성능 향상이 있었음을 의미한다.
- (2) 작은 용량을 갖는 ResNet-32나 MobileNet의 경우 DML에서 더 많은 이점 얻을 수 있었다.
- (3) 비록 WRN-28-10이 MobileNet이나 ResNet-32보다 훨씬 큰 모델일지라도 더 작은 peer(MobileNet이나 ResNet32)와 같이 학습했을 때에도 여전히 성능히 향상되는것을 확인 할 수 있다.
- (4) WRN-28-10과 같이 큰 네트워크 cohort를 학습시키는것은 단독 학습시키는것에 비해서 여전히 이점이 존재한다.
- 따라서 model distillation과 같은 기존의 방법과 반대로 큰 pre-trained teacher가 성능향상에 필수요소가 아니게 되며, 다수의 큰 네트워크들도 제안하는 distillation-like 과정을 통하여 성능이 향상된다.
3.3 Results on Market-1501
- Person re-identification task로 자세한 내용은 논문에서 확인..
3.4 Comparison with Distillation
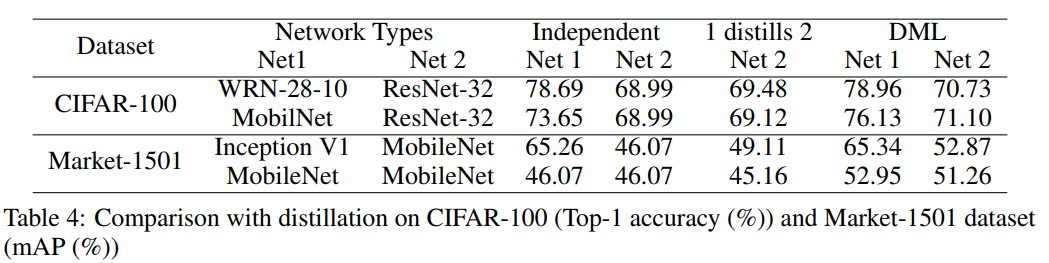
- 논문의 방법은 model distillation과 관련이 있기때문에 [7]과 같은 Distillation 방법과의 성능비교를 했다. Table 4는 student net(Net2)에 fixed posterior target을 제공하는 pre-trained teacher net(Net1)으로 구성된 model distillation과 DML 방식과 결과를 비교했다. 기대했던대로 성능 좋은 pre-trained teacher로부터 온 일반적인 distillation 방식은 student net이 단독학습하는것에 비해 더 나은 성능을 보여줬다(Table 4에서 1 distills 2 와 Net2 Independent의 비교). 하지만 실험결과를 보면 pre-trained teacher net이 필요가 없음을 알 수 있다. 표에서 확인 가능하듯이 “1 distills 2”와 “DML Net 2”의 결과를 비교해보면 두 네트워크를 DML 방식을 사용하여 학습시킨것이 distillation 방식에 비해 성능향상이 더 뚜렷했다. 이는 mutual learning 과정에서 teacher 역할을 하는 네트워크가 pre-trained되지 않은 student와의 상호작용을 통해 서로 학습함으로써 pre-trained 네트워크를 사용하는 방식에 비해 더 나은 결과를 보여준다는것을 의미한다. Finally, we note that on Market1501 training two compact MobileNets together provides a similar boost over independent learning compared to mutual learning with InceptionV1 and MobileNet: Peer teaching of small networks can be highly effective. In contrast, using the same network as teacher in model distillation actually makes the student worse than independent learning (the last row 1 distills 2 (45.16) vs. Net 2 Independent (46.07)).
3.5 DML with Larger Student Cohorts
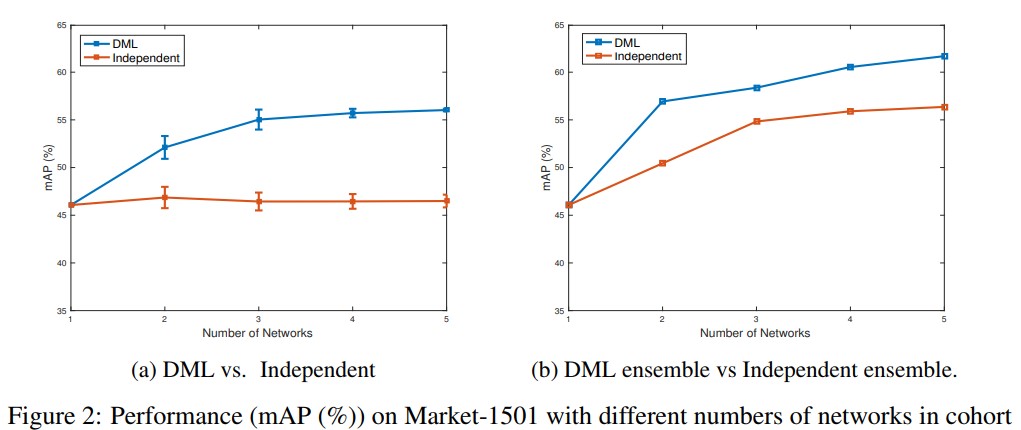
- 앞의 모든 연구는 2 student로 구성된 cohort를 이용하여 실험되었다. 이번 실험에선 student의 수에 따른 DML 성능에 대한 비교를 했다. Figure 2(a)는 MobileNets 구조를 사용하는 student에 대해 cohort size(student 수)가 증가함에 따른 Market-1501 데이터셋에 대한 DML training 실험결과를 보여준다. Figure 2(a)에서는 DML이 적용된 cohort의 network 수가 증가함에 따른 average single network의 mAP 성능이 향상되는것을 단독학습 된 경우와 비교하여 확인 할 수 있다. 이는 cohort의 peer의 수가 많아져 모델들이 같이 학슴함에 따라 student들의 generalization 능력이 강화된다는 것을 증명한다. From the standard deviations we can also see that the results get more and more stable with increasing number of networks in DML.
- 실험에서 사용하는 Independent 학습모델의 네트워크 수는 어떻게 저렇게 되는지 논문에서 정확히 정의되어있지 않음…앙상블 모델은 아닌듯함.
- 일반적으로 여러 네트워크를 학습시키는 기술은 그 네트워크들을 앙상블로 만들어 combined prediction을 만들도록 하는것이다. Figure 2(b)에서는 (a)와 동일한 구조를 갖는 네트워크에 대해 각 모델의 average prediction을 사용하는 대신 앙상블 모델(모든 멤버 의 concat된 feature 기반의 matching)을 사용하여 prediction했다. 실험 결과 앙상블 prediction이 예상대로 individual network의 성능을 넘어섰다(Fig 2.(b) vs (a)). 게다가 앙상블 prediction은 여러 네트워크를 cohort로 학습시킴으로써 더 나은 성능을 얻을 수 있었다(Fig. 2(b) DML ensemble vs. Independent ensemble). 앙상블 모델의 성능을 향상시키는 DML의 효과(Fig 2)를 볼 때 이 방법이 성능향상을 위한 일반적 방법인 앙상블 모델에 대해 최소한의 비용추가만 갖고도 성능을 향상시키는 general한 유용한 방법임을 실증한다.
3.6 How and Why does DML Work?
- 이 절에선 DML이 왜 효과가 있는지에 대해 설명한다. [4, 26, 9]같은 논문에선 “Why Deep Nets Generalize” 라는 주제를 다루는데, 이는 다음과 같은 insight를 준다. While there are often many solutions (deep network parameter settings) that generate zero train error, some of these generalise better than others due to being in wide valleys rather than narrow crevices [4, 9] – so that small perturbations do not change the prediction efficacy drastically; and that deep networks are better than might be expected at finding these good solutions [26], but that the tendency towards finding robust minima can be enhanced by biasing deep nets towards solutions with higher posterior entropy [4, 17].
Better Quality Solutions with More Robust Minima
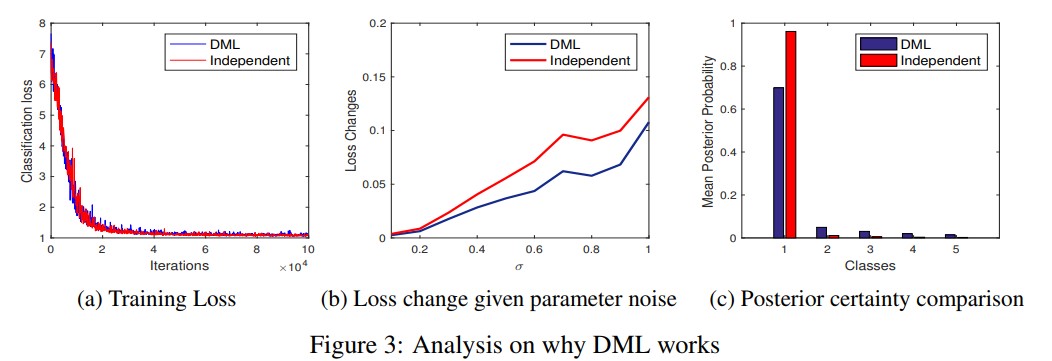
- 위의 insight로 인해 몇몇의 DML process에 대한 관측을 수행했다. 우선 논문의 적용에 대해 네트워크가 dratining data에 perfectly하게 맞춘다(training accuracy가 100%가 되고 classification loss가 Fig 3(a)처럼 낮아짐). 하지만 앞에서 언급한것처럼 DML은 test data에 대해 더 잘 작동한다. 따라서 traning loss에서 더 deep한 minima를 찾도록 하는것이 아니라 DML가 test set에 대해 더 generalize를 잘하는 wider하고 robust한 minima를 찾도록 도와준다는 것이다. [4, 9]에서 감명받아 MobileNet을 이용해 Market-1501에 대해 발견된 minima의 robusteness를 test하는 간단한 실험을 했다. DML과 단독학습한 모델의 경우 각 모델의 파라미터에 대해 variable standard deviation $\rho$의 independent Gaussian noise를 추가하기 전과 후의 각 모델에 대한 training loss를 비교한다. We see that the depths of the two minima were the same (Fig. 3(a)), but after adding this perturbation the training loss of the independent model jumps up while the loss of the DML model increases much less. 이는 DML 모델이 더 넓은 minima를 찾음을 의미하며 이는 곧 generalization 성능이 좋다는것을 의미한다[4, 17].
How a Better Minima is Found
- 어떻게 DML이 이러한 더 나은 minima를 찾도록 도와주나? When asking each network to match its peers probability estimates, mismatches where a given network predicts zero and its teacher/peer predicts non-zero are heavily penalised. Therefore the overall effect of DML is that, where each network independently would put a small mass on a small set of secondary probabilities, all networks in the DML tend to aggregate their prediction of secondary probabilities, and both (i) put more mass on the secondary probabilities altogether, and (ii) place non-zero mass on more distinct secondary probabilities. 이러한 효과를 Figure 3.(c)에서 ResNet-32 on CIFAR-100 trained by DML과 independently trained ResNet-32간에 top-5 highest ranked classes의 probability들을 비교하여 설명해놨다. For each training sample, the top 5 classes are ranked according to the posterior probabilities produced by the model (Class 1 being the true class and Class 2 the second most probable class, so on and so forth). Here we can see that the assignment of mass to probabilities below the Top-1 decays much quicker for Independent than DML learning. This can be quantified by the entropy values averaged over all training samples of the DML trained model and the independently trained model being 1.7099 and 0.2602 respectively. Thus our method has connection to entropy regularisation-based approaches [4, 17] to finding wide minima, but by mutual probability matching on ‘reasonable’ alternatives, rather than a blind high-entropy preference.
DML with Ensemble Teacher
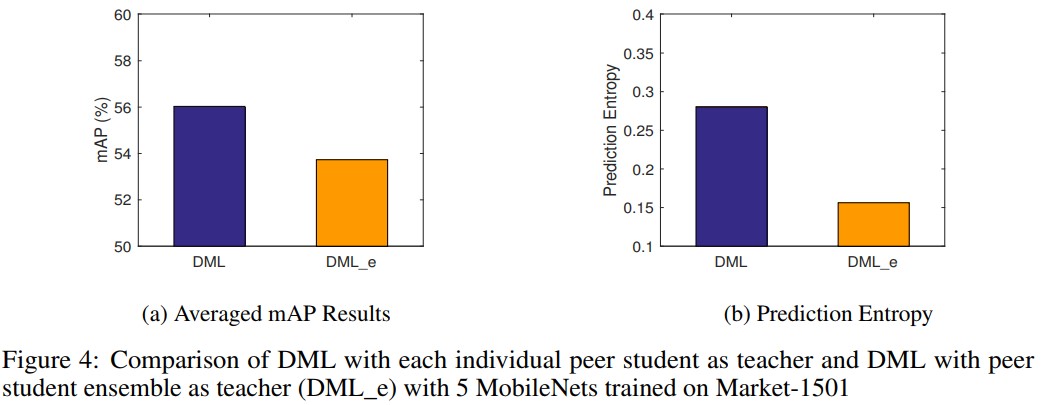
- In our DML strategy, each student is taught by all other students in the cohort individually, regardless how many students are in the cohort (Eq. (10)). In Sec. 2.3, an alternative DML strategy is discussed, by which each student is asked to match the predictions of the ensemble of all other students in the cohort (Eq. (11)). One might reasonably expect this approach to be better. As the ensemble prediction is better than individual predictions, it should provide a cleaner and stronger teaching signal – more like conventional distillation. In practice the results of ensemble rather than peer teaching are worse (see Fig. 4 (a)). By analysing the teaching signal of the ensemble in comparison to peer teaching, the ensemble target is much more sharply peaked on the true label than the peer targets, resulting in larger prediction entropy value for DML than DML_e (see Fig. 4 (b)). Thus while the noise-averaging property of ensembling is effective for making a correct prediction, it is actually detrimental to providing a teaching signal where the secondary class probabilities are the salient cue in the signal and having high-entropy posterior leads to more robust solutions to model training.
Conclusion
- 논문에선 DNN을 집단(cohort)으로 만들어 peer와 mutual distillation 을 통해 DNN의 성능을 향상시키는 간단하지만 general하게 적용 가능한 방법을 제안하였다. 이 방법을 이용해 static(단독학습, pre-trained) teacher로부터 distilled된 네트워크보다 성능이 더 좋은 compact network를 얻을 수 있었다. Deep mutual learning(DML)을 활용하는 한가지 예로 compact하고 빠른 효율적인 네트워크를 얻을 수 있다. 또한 논문에선 이 방식을 이용해 크고 powerful한 네트워크의 성능도 향상시킬 수 있었으며, 논문에서 제안하는 방식을 따라 학습된 network cohort(네트워크 그룹)은 더 성능 향상을 위한 앙상블 모델로 사용될 수 있다.

 Seongkyun Han's blog
Seongkyun Han's blog