Learning Efficient Object Detection Models with Knowledge Distillation
08 Apr 2019 | Deep learningLearning Efficient Object Detection Models with Knowledge Distillation
Original paper: https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6676-learning-efficient-object-detection-models-with-knowledge-distillation.pdf
Authors: Guobin Chen, Wongun Choi, Xiang Yu, Tony Han, Manmohan Chandraker
Abstract
- CNN을 이용하여 object detector의 성능이 크게 향상되었지만, 연산시간또한 크게 증가하게 되는 단점이 존재했다. SOTA 모델들은 매우 deep하고 많은 파라미터들을 갖는 구조를 사용한다. 이러한 모델들의 파라미터 수를 줄이는 연구들이 많이 수행되었지만, 성능또한 같이 줄어드는 단점이 존재했다. 본 논문에서는 knowledge distillation[20]과 hint learning[34]을 이용하여 정확도가 향상된 compact하고 fast한 object detection network의 학습을 위한 framework를 제안한다. 앞선 연구인 knowledge distillation에서는 간단한 classification task에 대한 성능 향상만을 보였다. 하지만 object detection의 경우 regresson, region proposal과 less boluminous label등의 challenging한 문제들이 존재한다. 논문에선 이러한 문제들에 대한 개선을 위해 class imbalance 해결을 위한 weighted cross-entropy loss, regression component를 해결하기 위한 teacher bounded loss, 그리고 intermediate teacher distributions을 더 잘 학습하기 위한 adaptation layer등을 제안한다. 실험에선 PASCAL, KITTI, ILSVRC, MS-COCO 데이터셋을 이용하여 다른 distillation configuration들에 대한 실험을 진행했으며, 일반적인 mAP의 측정으로 평가되었다. 실험 결과는 최근의 multi-class detection models에 대한 accuracy-speed trade-off의 향상을 보여준다.
1. Introduction
- CNN등의 발전으로 인해 object detection의 성능은 매우 많이 발전했지만, 실제로 이를 적용하기에는 속도가 너무 느린 단점이 존재했다. 많은 연구들이 정확한 객체검출기 모델의 개발을 위해 진행되었지만 모두 deep한 구조를 사용함으로 인해 runtime의 computational expense가 증가했다. 하지만 이는 deep neural network들이 일반화를 위한 over-parameterized 문제로 알려져있다. 따라서 속도 향상을 위해 몇몇의 연구에선 새로운 구조의 fully convolutional network를 만들어 이를 해결하고자 하거나 작은 filter와 적은 channel을 이용해 파라미터 수를 줄여보고자 했다[22, 25]. 이로인해 객체검출기의 속도가 매우 빨라졌지만 아직도 real-time으로 사용하기엔 무리가 있고 성능향상을 위한 tunning이나 까다로운 redesign등이 필요하다.
- 표현력이 충분한 deep 네트워크의 경우 학습이 잘 되면 더 나은 성능을 보여준다. 하지만 적은 class를 위한 객체검출 모델들은 이런 표현력이 큰 모델이 필요없다. 이로인해 [9, 26, 41, 42]논문에선 모델 압축을 이용해 layer-wise reconstrunction을 따라 각 레이어의 weight를 분해하거나 fine-tunning을 이용해 정확도를 조금 올리게 된다. 이러한 방법들로 인해 속도는 많이 향상되지만 여전히 original model과 압축된 모델간의 성능차가 존재하며, object detection에 이를 적용할 경우 압축모델과 원래모델의 성능차이는 더 벌어지게 된다. 반면 knowledge distillation이 적용된 연구들의 경우 깊고 복잡한 모델의 behavior를 흉내내도록 shallow or compressed 모델이 학습되어지며 knowledge distillation을 통해 대개의 모델들이 정확도 하락을 복구하게 된다[3, 20, 34]. 하지만 이러한 결과들은 dropout과 같은 strong regularization도 적용하지 않고 간단한 네트워크를 이용해 간단한 classification문제에 대한 결과만들 보여준다.
- Distillation을 복잡한 multi-class object detection에 적용하기에는 아래의 몇몇 문제가 따른다. 우선, 객체검출 모델의 성능은 모델 압축 시 classification 모델에 비해 성능이 더 떨어지게 된다. 이는 detection label이 더 expensive 하고 양이 많지 않기 때문이다(expensive and less boluminous). 두번째로, 모든 class가 동등하게 중요하다고 가정되는 classification을 위해 distillation이 제안되지만, object detection과 같이 background class가 훨씬 더 많이 사용되는 경우에는 knowledge distillation이 별 소용이 없게된다. 세번째로, detection은 각 classification과 bounding box regression을 한데로 묶는 복잡한 task이다. 마지막으로, 추가 challenge로써 다른 도메인의 데이터(high-quality and low-quality image domains, or image and depth domains)에 의존하는 다른 task와는 다르게 추가 데이터나 label이 없이 동일한 도메인(images of the same dataset) 내에서 정보(knowledge)를 이전하는데에 집중하는것이다.
- 위의 challenges에 대해 논문에선 knowledge distillation을 이용한 fast object detection 모델의 학습을 위한 방법을 제안한다. 논문의 main contributions는 아래에 있다.
- Knowledge distillation을 이용한 compact multi-class object detection 모델의 end-to-end 학습 framework를 제안한다(section 3.1). 아는바로는 이게 첫 번째 성공적인 multi-class object detection의 knowledge distillation의 적용이다.
- 앞에서 말한 challenges를 효과적으로 다루는 새로운 loss를 제안한다. 세세적으로 object class의 반대인 background class를 위한 misclassification의 impact의 imbalance를 계산하는 classification을 위한 weighted cross entropy loss 를 제안한다(section 3.2). 다음으로 knowledge distillation을 위한 teacher bounded regression loss 를 제안하며(section 3.3) 마지막으로 teacher의 intermediate layer의 neuron에서의 distribution을 student가 학습하도록 해주는 adaptation layers for hint learning 을 제안한다(section 3.4).
- Public benchmark를 이용하여 제안하는 모델을 평가한다. 모든 benchmark에 대해 성능이 모두 향상되었다. 각 제안하는 방법에 대해 모두 성능이 향상되었다(section 4.1 - 4.3).
- 논문에서 제안하는 framework에 대해 generalization과 under-fitting problem에 관련된 insight를 제안한다.
2. Related Works
- CNNs for Detection. Deformable Part Model (DPM) [14] was the dominant detection framework before the widespread use of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Following the success of CNNs in image classification [27], Girshick et al. proposed RCNN [24] that uses CNN features to replace handcrafted ones. Subsequently, many CNN based object detection methods have been proposed, such as Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) [19], Fast R-CNN [13], Faster-RCNN [32] and R-FCN [29], that unify various steps in object detection into an end-to-end multi-category framework.
- Model Compression. CNNs are expensive in terms of computation and memory. Very deep networks with many convolutional layers are preferred for accuracy, while shallower networks are also widely used where efficiency is important. Model compression in deep networks is a viable approach to speed up runtime while preserving accuracy. Denil et al. [9]은 인공신경망이 때때로 과하게 parameterized 되므로 중복되는 parameter들에 대해 제거가 가능한 것을 증명한다. Subsequently, various methods [5, 7, 10, 15, 17, 30] have been proposed to accelerate the fully connected layer. Several methods based on low-rank decomposition of the convolutional kernel tensor [10, 23, 28] are also proposed to speed up convolutional layers. To compress the whole network, Zhang et al. [41, 42] present an algorithm using asymmetric decomposition and additional fine-tuning. 유사하게 Kim et al.[26]은 one-shot whole network compression을 제안하였으며, 정확도의 큰 하락 없이 1.8배의 속도가 향상되었다. 실험에서는 [26]에서 제안한 방법을 사용했다(Compression of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Fast and Low Power Mobile Applications). Besides, a pruning based approach has been proposed [18] but it is challenging to achieve runtime speed-up with a conventional GPU implementation. Additionally, both weights and input activations can be the quantized( [18]) and binarized ( [21, 31]) to lower the computationally expensive.
- Knowledge Distillation. Knowledge distillation is another approach to retain accuracy with model compression. Bucila et al. [3] propose an algorithm to train a single neural network by mimicking the output of an ensemble of models. Ba and Caruana [2] adopt the idea of [3] to compress deep networks into shallower but wider ones, where the compressed model mimics the ‘logits’. Hinton et al. [20] propose knowledge distillation as a more general case of [3], which applies the prediction of the teacher model as a ‘soft label’, further proposing temperature cross entropy loss instead of L2 loss. Romero et al. [34] introduce a two-stage strategy to train deep networks. In their method, the teacher’s middle layer provides ‘hint’ to guide the training of the student model.
- Other researchers [16, 38] explore distillation for transferring knowledge between different domains, such as high-quality and low-quality images, or RGB and depth images. 본 논문의 연구방향과 비슷하게 Shen et al.[36]에선 distillation과 hint framework에 대한 compact object detection model의 학습의 영향에 대하여 연구를 했다. 하지만 앞의 방법은 pedestrian(보행자) object detection task에 대하여만 진행된 연구이므로, 이는 multi-category object detection에는 general하게 적용하지 못한다. [36]과는 다르게 제안하는 방법은 multi-category object detection에 적용 가능하다. 게다가 [36]은 외부 region proposal 방법을 사용하지만 논문의 방법은 distillation과 hint learning이 최근의 end-to-end object detection framework의 region proposal과 classification 모두에 적용 가능함을 보인다.
3. Method
- 본 논문에선 Faster-RCNN[32]를 meth-architecture로 사용했다. Faster-RCNN is composed of three modules: 1) A shared feature extraction through convolutional layers, 2) a region proposal network (RPN) that generates object proposals, and 3) a classification and regression network (RCN) that returns the detection score as well as a spatial adjustment vector for each object proposal. 각 RCN과 RPN 모두 1)의 출력을 사용하며, RCN은 RPN의 출력을 입력으로 사용한다. 정확한 객체검출을 위해 앞의 세 요소에 대해 표현력 strong한 모델을 학습하는것이 중요하다.
3.1 Overall Structure
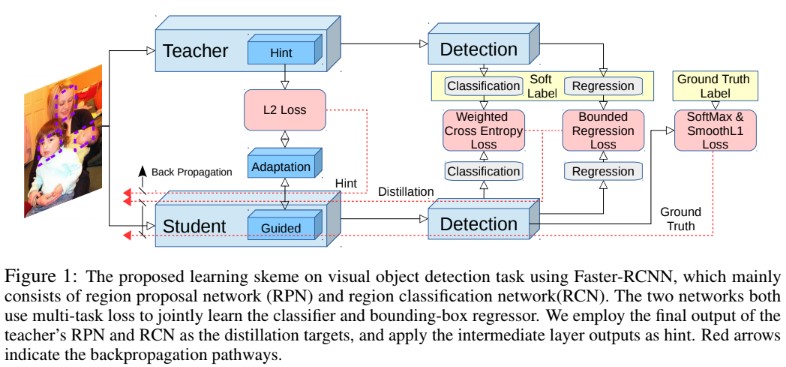
- 논문에서 제안하는 세 가지 component를 이용해 high capacity를 갖는 teacher의 정보를 이용해 효율적인 student 객체검출기를 학습시켰다. Figure 1에선 전체적인 framework를 확인할 수 있다. 우선 hint based learning[34] (section 3.4)에선 teacher net의 feature를 닮도록 student net의 feature가 만들어지게한다. 다음으로 knowledge distillation framework [3, 20]을 이용해 RPN과 RCN classification module을 학습시킨다. Object detection의 severe category imbalance문제 해결을 위해 distillation framework에 weighted cross entropy loss를 적용했다. 마지막으로 teacher의 regression output을 student가 upper bound로 사용하게끔 transfer 했으며 만약 student의 regression output이 teacher의 것보다 더 낫다면 추가적인 loss는 적용되지 않는다. 전체적인 학습에서의 objective는 아래와 같다.
(1)
- N은 RCN, M은 RPN의 batch size이다. $L_{cls}$ 는 ground truth를 이용한 hard softmax loss와 (2)의 soft knowledge distillation loss[20]의 조합으로 구성되어있다.$L_{reg}$ 는 smoothed L1 loss[13] 과 논문에서 제안하는 (2)의 teacher bounded L2 regression loss로 구성된 bounding box regression loss이다. 마지막으로 $L_{hint}$ 는 teacher의 feature response를 student가 닮도록 하는 hint based loss function이며 (6)에 설명되어있다.
3.2 Knowledge Distillation for Classification with Imbalanced Classes
- 분류기 모델의 학습을 위해 knowledge distillation이 제안되어 사용되었다. 만약 ${x_{i}, y_{i}},\; i=1, 2, …, n$ (where $x_{i}\in \mathfrak{J}$, $\mathfrak{J}$ 는 input image, $y_{i}\in \mathfrak{Y}$, $\mathfrak{Y}$는 해당하는 class label) 이라는 datasset이 있다고 해보자. $t$는 teacher model이며 $P_{t}=softmax(\frac{Z_{t}}{T})$는 teacher의 prediction, $Z_{t}$는 final score ouput이라고 하자. $T$는 temperature parameter(일반적으로 1로 설정)이다. 유사하게 $P_{s}=softmax(\frac{Z_{s}}{T})$는 student 네트워크 $s$의 prediction이다. Student network $s$는 아래의 loss function을 optimize하도록 학습된다.
(2)
- $L_{hard}$는 Faster-RCNN의 ground truth label을 사용하는 hard loss이며 $L_{soft}$는 teacher의 prediction을 사용하는 soft loss, $\mu$는 hard와 soft loss의 balancing을 위한 파라미터이다. 보통은 deep 네트워크가 성능이 좋다. Soft label은 teacher에 의해 찾아진 다양한 클래스간의 관계에 대한 정보가 포함되어있다. Soft label을 이용한 학습에서 student network는 이러한 hidden정보들을 전달받게된다.
- [20]에서 각 hard와 soft loss들은 cross entropy loss이다. 하지만 간단한 classification 문제와는 다르게 detection task는 심각한 서로다른 카테고리간의 imbalance를 고려해야하며, 이는 background로 분류되어야 하는 카테고리가 너무 많음을 의미하게된다. 분류기 모델의경우 발생가능한 오류는 foreground(detection 안의 bounding box쳐진 안 내용의) 오분류 뿐이다. 하지만 detection task는 background와 의미있는 foreground의 오분류는 매우 주요하며 foreground의 오분류는 매우 드물다. 이를 조절하기 위해 class-weighted cross entropy를 distillation loss로써 적용하였다. 식은 아래와 같다.
(3)
- weight parameter인 $w_c$에 대해 논문에선 background class에 대해 큰 weight를 사용하였으며 다른 class들은 비교적 작은 weight를 사용했다. 예를 들어 PASCAL dataset에 대해 background class에 대해 $w_{0}=1.5$를, 다른 foreground class들에는 $w_{i}=1$을 사용했다.
- $P_{t}$가 hard label과 매우 유사할 때 (하나의 class만 1에 매우 가깝고 나머지들은 0에 매우 가까운 경우) temperature parameter $T$는 softmax output을 soften하게 만들게 하기 위해 사용된다. 큰 temperature parameter를 사용할 경우 네트워크는 더 soft한 결과를 최종단에서 출력하게 되며 이를통해 거의 0에 가까운 softmax를 거친 결과가 cost function에서 무시되지 않도록 해준다. 이는 MNIST classification같이 매우 간단한 task에 적절하다. 하지만 prediction error가 이미 높은 어려운 문제같은 경우 큰 temperature parameter의 사용은 학습에 좋지않은 noise가 더 많이 생기게 한다. 따라서 작은 $T$가 [20]에선 큰 데이터셋에 대한 실험에 사용되었다. object detection과 같이 더 어려운 문제의 경우 distillation loss의 temperature parameter를 사용하지 않는것이($T=1$) 실제 가장 잘 작동한다는것을 알 수 있었다.(보충자료 참조)
3.3 Knowledge Distillation for Regression with Teacher Bounds
- Classification layer에서 대부분의 CNN detector들[26, 29, 32, 33]은 input proposal의 size와 location을 조절하기 위해 사용한다. 때때로 좋은 regression 모델을 학습하는것이 object detector의 정확도를 보장하는데에 중요하다. Discrete category들의 distillation과 다르게 teacher의 regression output은 unbounded real valued regression output으로 인해 student model에게 매우 잘못된 guidance를 제공할 수 있다. 게다가 teacher는 ground truth와 모순되는 방향으로 regression direction 정보를 줄 수도 있다. 따라서 target(student)에서 teacher의 regression output을 그대로 사용하기보다는 student가 잘 학습하도록 upper bound로써 사용하도록 설정하였다. Student의 regression vector는 일반적으로 GT label과 가능하면 최대한 가깝도록 되어야하지만 특정 margin을 갖는 teacher의 추론보다 정확하게 된다면 student는 추가적인 loss없이 자신의 추론결과로만 학습하게 된다.(student의 추론이 teacher보다 정확하면 teacher에 의한 loss값 반영 없이 자체결과로만 학습) 논문에선 이를 teacher bounded regression loss 라 하며 $L_{b}$로 정의하고 아래와 같이 정의한다. $L_{b}$ 는 regression loss $L_{reg}$에서 사용된다.
(4)
- 수식에서 $m$은 margin, $y_{reg}$는 regression ground truth label, $R_{s}$는 student network의 regression output, $R_{t}$는 teacher network의 prediction, $\mathcal{V}$는 weight parameter(실험에선 0.5로 설정)다. $L_{sL1}$은 [13]의 smooth L1 loss이다. Teacher bounded regression loss $L_{b}$는 student의 error가 teacher의것보다 클 때 network를 penalize한다(loss가 증가함을 의미). $L_{b}$에서 L2 loss를 사용하지만 L1이나 smoothed L1과 같은 다른 regression loss도 $L_{b}$와 결합 가능하다. 이렇게 조합된 loss는 student가 teacher와 가깝거나 혹은 더 나은 regression을 만들도록 하며 만약 teacher의 성능에 도달할경우 student를 너무 많이 push하지 않게한다.
3.4 Hint Learning with Feature Adaptation
- Distillation의 경우 final output만을 이용해 정보를 전달한다. [34]에서는 teacher의 중간 representation을 사용하는것이 학습과정에서 hint 로서 작용해 student의 성능이 더 좋아진다고 한다. 그들은 feature vector V와 Z에 대해 L2 distance를 사용했다.
(5)
- 수식에서 Z는 hint로 사용할 teacher의 중간 레이어에서의 feature, V는 student에서 guided될 레이어의 출력 feature를 의미한다. 또한 L1 loss를 사용하여 평가한다.
(6)
- Hint learning을 적용할 때 사용될 student와 teacher의 뉴런 수, 즉 channels, width, height가 동일해야 한다. Hint와 guided layer의 채널 수를 맞추기 위해 출력 크기가 hint layer와 동일한 adaptation layer를 guided layer 뒤에 추가하였다. Adaptation layer는 student가 만들어낸 feature가 teacher와 동일하도록 하는 뉴런 수를 갖는 레이어다. 두 hint와 guided layer라 fully connected layer일 경우 adaptation layer도 fully connected layer가 된다. Hint와 guided layer가 convolutional layer일 경우 1x1 convolution을 사용하여 메모리 소모를 줄였다. 흥미롭게도 hint와 guided layer의 채널 수가 같더라도 adaptation layer를 적용하는것이 효율적인 knowledge transferring에 중요한것을 확인했다(section 4.3). 또한 adaptation layer는 hint와 guided layer의 feature 형식이 다른 경우에도 적용하여 matching 시킬 수 있다. Hint나 guided layer가 convolutional이고 hint와 guided layer의 해상도(크기)가 다른 경우 (VGG16과 AlexNet 비교같이) [16]의 padding trick을 이용하여 출력의 수를 맞추었다.
4. Experiment
- In this section, we first introduce teacher and student CNN models and datasets that are used in the experiments. 다양한 데이터셋에 대한 전체 결과는 section 4.1에서 보여진다. Section 4.2에선 제안하는 방법을 더 작은 네트워크와 lower quality input을 이용한 실험결과를 보여준다. Section 4.3에서는 classification/regression, distillation 및 hint learning의 세 가지 component에 대한 albation study를 설명한다. Distillation, hint learning에 대해서 얻어진 insight는 section 4.4에서 다뤄진다. Details에 대해선 supplementary materials에서 설명된다.
Datasets
- We evaluate our method on several commonly used public detection datasets, namely, KITTI [12], PASCAL VOC 2007 [11], MS COCO [6] and ImageNet DET benchmark (ILSVRC 2014) [35]. Among them, KITTI and PASCAL are relatively small datasets that contain less object categories and labeled images, whereas MS COCO and ILSVRC 2014 are large scale datasets. KITTI와 ILSVRC 2014 데이터셋은 test set의 ground-truth annotation을 제공하지 않으므로 [39]와 [24]의 tranining/validation을 사용했다. For all the datasets, we follow the PASCAL VOC convention to evaluate various models by reporting mean average precision (mAP) at IoU = 0.5 . For MS COCO dataset, besides the PASCAL VOC metric, we also report its own metric, which evaluates mAP averaged for IoU 2 [0.5 : 0.05 : 0.95] (denoted as mAP[.5, .95]).
Models
- 일반적인 구조인 AlexNet[27], AlexNet with Tucker Decomposition[26], VGG16[37], VGGM[4]를 teacher/student model의 CNN 구조로 사용했다. 각 student와 teacher 쌍에 대해 두개의 다른 settings를 적용했다. 첫 번째 실험 set에서 작은 네트워크(less parameters)를 student로, 큰 모델을 teacher로 사용하였다(예를 들어 AlexNet을 student로, VGG16을 teacher로 사용). 두 번째 실험 set에서는 네트워크의 구조를 유지하면서 작은 크기의 영상을 student model로 넣고, 큰 사진을 teacher model의 input으로 넣었다.
4.1 Overall Performance
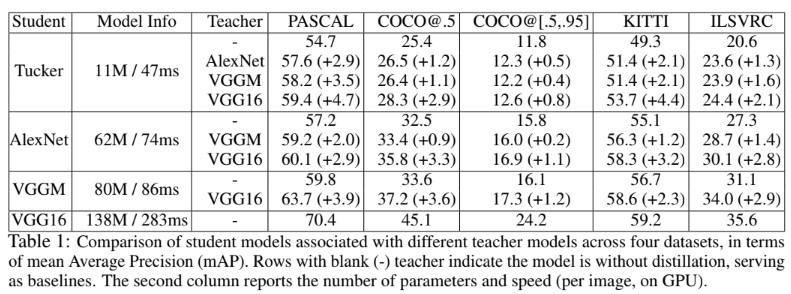
- Table 1은 다른 teacher model의 구조와 student model의 구조에 대한 mAP를 실험결과에 따라 비교한 결과이다. Teacher model을 사용하지 않는 실험의 경우 가장 나은 정확도가 나은 결과를 실어놓았다. 파라미터 수가 많은 크고 깊은 모델의 성능이 작고 shallow한 모델에 비해 성능이 좋았지만 속도는 작은 모델이 큰것보다 더 빨랐다.
- Teacher와 student architecture의 차이에 불구하고 모든 dataset에 대해 distillation과 hint learning이 적용된 모델의 성닝이 더 향상되었다. Student model에 fixed scale(number of parameters)을 사용한 경우 자체적으로 from scratch training이나 fine-tunning은 최선의 선택이 아니다. 더 성능 좋은 teacher로 모델을 학습시킬 경우 student의 성능은 더 향상된다. 즉, 더 deep한 teacher가 전달해주는 정보(knowledge)가 student에겐 더 informative한 정보가 된다. 참고로 VGG16기반의 Tucker model은 alexnet보다 5배가량 모델 크기가 작지만 PASCAL datset에 대해 훨씬 높은 정확도의 향상이 있었다. 이는 CNN 기반 object detector가 매우 over-parameterized 되었음을 의미한다(효율이 낮음). 반대로 데이터셋의 크기가 큰 경우 복잡한모델의 성능을 뛰어넘는 결과를 만들기 더 어려웠다. 이는 큰 크기의 데이터셋을 위해선 용량(capacity)이 큰 모델이 적합함을 의미한다. 일반적으로 효율 측정에 있어서 KITTI dataset에 대해 VGG 16 teacher에서 AlexNet student로 3배 더 빠르다(영어로, Typically, when evaluating efficiency, we get 3 times faster from VGG16 as teacher to AlexNet as student on KITTI dataset. 문장이 엉터리다.). 자세한 정보는 supplementary material에서 확인바란다.
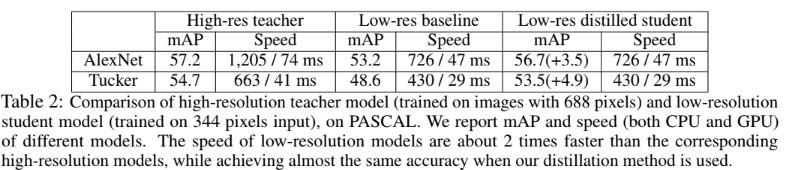
- 또한 [38]과 유사하게 또다른 student-teacher mode에 대해 연구했다. Teacher와 student가 완전히 동일한 구조를 유지하면서 student에겐 down-scaled image를 입력으로, teacher는 고해상도 이미지를 입력으로 줬다. 최근 연구[1]에서 입력 영상의 해상도가 object detection 성능에 큰 영향을 끼친다고 한다. 반면 downsampling된 이미지는 quadratically(2차적으로)하게 conv 연산량을 줄이고 속도를 향상시켰다. Table 2에서 PASCAL VOC dataset의 input size를 반으로 줄이고 student net에 넣었고, teacher에는 original 해상도 영상을 넣었을 때, teacher와 비교하여 student의 정확도는 거의 유지됨과 동시에 2배는 빠르게 동작하였다.(이상적으로 convolutional layer의 연산은 4배 빠르나 loading overhead와 다른 layer에서의 관련없는 연산들때문에 2배의 속도 향상에 그치게 됨)
4.2 Speed-Accuracy Trade off in Compressed Models
- It is feasible to select CNN models from a wide range of candidates to strike a balance between speed and accuracy. However, off-the-shelf CNN models still may not meet one’s computational requirements. Designing new models is one option. But it often requires significant labor towards design and training(연산량 조절을 위해 새 모델을 설계해야 하지만 노동력이 많이 든다는 뜻). 학습된모델은 특정한 task를 위해서만 학습되었으므로 속도와 정확도의 trade-off를 고려하여 조절하는것은 또 다른 일이 되며 새 모델을 학습시키는것도 일이다. 이로 인해 distillation은 또 다른 attractive option이 될 수 있다
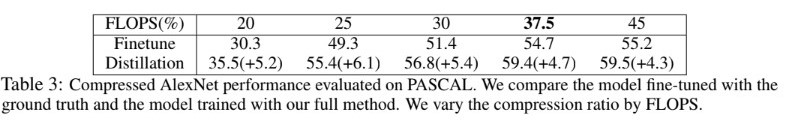
- Object detection의 knowledge distillation 적용을 위한 speed-accuracy trade off를 이해하기 위해 Tucker decomposition이 적용된 AlexNet의 compression ratio(the ranks of weight matrices)를 변화시켜가며 실험했다. CNN의 FLOPS를 이용하여 compression ratio를 측정했다. Table 3은 압축된 크기가 원본의 20%가 되는 경우처럼 네트워크가 너무 많이 압축될 때 정확도가 57.2에서 30.3으로 급격하게 떨어지는것을 확인 할 수 있었다(table 2와 3 같이 확인필요). 하지만 제안하는 distillation framework가 적용되지 않은 squeezed network의 정확도는 37.5% 압축에 대해 finetune의 54.7%에 불과했다. 반면에 제안하는 방법을 적용한 경우 VGG16과 같은 deep teacher와 함께 정확도를 59.4%까지 향상시켰으며, 이는 압축되지 않은 AlexNet 모델의 57.2%보다 좋은 결과이다.
4.3 Ablation Study
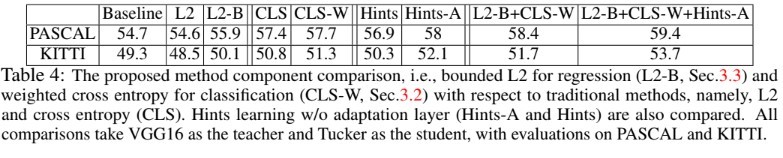
- Table 4에서 보여지듯, 제안하는 novel loss의 효과를 확인하기 위해 서로다른 distillation과 hint learning에 대한 비교실험을 수행했다. VGG16을 teacher로, Tucker를 student model로 모든 실험에서 통일했다. 다른 선택지들은 유사한 trend를 반영했다. Faster-RCNN에서 proposal classification과 bounding box regression은 두 main task이다. 일반적으로 classification은 cross entropy loss로 구성되며 Table 4에서 CLS로 정의되며 bounding box regression은 L2 loss로 regularized되며 L2로 Table 4에 나타난다.
- Objective function에 의해 적은 확률값을 갖는 클래스가 무시되어지는것을 막기 위해 high temperature를 갖는 soft label, 즉 weighted cross entropy loss가 section 3.2에서 proposal classification task를 위해 제안되었다. Table 4에선 section 3.2의 (3)에서 제안된 weighted cross entropy loss(CLS-W)를 standard cross entropy loss(CLS)와 비교하며 PASCAL과 KITTI dataset 모두에서 약간의 성능 향상을 확인할 수 있다.
- Bounding box regression에 대해서, 단순하게 student가 teacher의 출력을 따라하도록 하는것은 labeling noise에 의해 악영향을 미치게 된다. 이를 개선하기 위해 section 3.3의 (4)를 제안하였으며 이는 teacher의 예측이 student를 guide하도록 boundary로써작용한다. 이러한 방법으로 인해 Table 4의 L2-B에서 L2의 방법에 비해 1.3%이상의 정확도 향상이 있었다. 참고로 1%의 object detection 정확도 향상은 매우 큰것이며, 특히 많은 영상을 포함하는 large-scale dataset에서는 더 그렇다.
4.4 Discussion
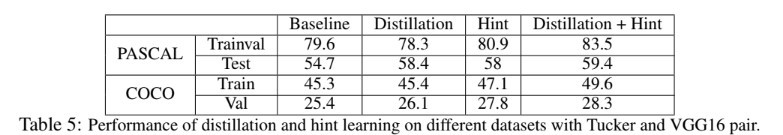
- 이 단원에선 distillation과 hint learning에 대한 insight에 대해 다룬다. Table 5는 PASCAL과 COCO dataset의 trainval과 testing set에 대하여 VGG16의 정보로부터 학습된 Tucker model의 정확도를 비교한다. 일반적으로 distillation은 student의 generalization capability를 향상시키며 hint learning은 training과 testing 정확도 모두 향상하도록 도와준다.
Distillation improves generalization
- [20]에서 다뤄진 image classification과 비슷하게 object detection task의 label간의 구조적인 relationship도 존재한다. 예를 들어서 ‘Car’는 ‘Person’보다 ‘Truck’ 클래스와 비슷한 시각적 특징을 공유한다. 이러한 구조적 정보는 ground truth annotation에 포함되어있지 않다. 따라서 high capacity를 갖는 teacher로부터 학습된 relational information을 student로 주입하는것은 detection model의 일반화 능력을 향상시키는데 도움이 될 것이다. Table 5에서는 distillation을 적용한 결과 모두 testing accuracy 성능이 향상 된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Hint helps both learning and generalization
-
CNN based object detection task에서 under-fitting은 흔한 문제점이다. 간단한 분류와는 다르게 정확도가 많이 낮다. 이는 학습 알고리즘이 saddle point(minima)를 찾는데에 문제가 있는것으로 판단된다[8]. 반대로 hint는 intermediate layer에서의 guidance를 직접적으로 사용하여 이러한 문제를 피할 수 있다. 따라서 hint learning을 사용하여 학습된 모델은 training과 testing에서 모두 정확도가 향상된다.
-
마지막으로 distillation과 hint learning을 조합하는 경우 training과 test 정확도 모두 기존의 방법에 비해 크게 향상되었다. Table 5는 실험적으로 PASCAL과 MS-COCO에 대해 제안하는 방법이 효과가 있음을 보여준다. 제안하는 방법이 또한 face similar generalization이나 under-fitting problem에도 적용 가능 할 것이라 생각된다.
Conclusion
- 논문에선 knowledge distillation을 이용한 compact하고 빠른 CNN based object detector의 학습 framework를 제안했다. 매우 복잡한 teacher detector를 guide로 하여 효율적인 student model을 학습시켰다. Knowledge distillation, hint framework와 제안하는 loss function을 이용하였을 때 다양한 실험 setup에 대하여 모두 성능이 향상되었다. 특히 제안하는 framework로 학습된 compact model은 PASCAL VOC 데이터셋에 대한 teacher model의 정확도와 매우 비슷한 수준으로 훨씬 빠르게 동작하였다. 논문의 실험을 통해 object detector의 학습에 under-fitting 문제가 있음을 확인했으며, 이는 해당 연구분야에서 더 연구 가능한 insight를 준다.

 Seongkyun Han's blog
Seongkyun Han's blog